{survival} package
(AST405) Lifetime data analysis
Time-to-event data
-
Time-to-event data are defined as \(\{(t_i, \delta_i), i=1, \ldots, n\}\)
\(t_i\,\rightarrow\) observed time
\(\delta_i\,\rightarrow\) censoring indicator (1=failure, 0=censored)
- Defining time and censoring indicator in
Rfor the following sample of five observations \[ 20, 13^+, 10, 25, 18^+ \]
dat0# A tibble: 5 × 2
time status
<dbl> <dbl>
1 20 1
2 13 0
3 10 1
4 25 1
5 18 0
survival package
There are a number of R packages available for analyzing time-to-event data
The
survivalpackage will be used for the course, the current (January 2025) version of survival package is 3.8-3-
Author, contributors, and maintainer of survival package
Terry M Therneau [aut, cre]
Thomas Lumley
Atkinson Elizabeth
Crowson Cynthia
Creating survival objects and curves
-
survival::survfit()function is used to obtain non-parametric estimate survivor function
survfit(Surv(time, time2, event) ~ x, data)Surv\(\rightarrow\) creates a survival object, which has arguments such as,time,time2,event, andtype(censoring type “right”, “left”, “interval”, etc.)time\(\rightarrow\) observed time (numeric object)event\(\rightarrow\) censoring status (1=failure, 0=censored)x\(\rightarrow\) strata (categorical variable),x=1when stratified analysis is not required (single curve)
-
Some important arguments of
survfit()functionstype\(\rightarrow\) 1 (direct estimation of survivor function), 2 (survivor function estimated from cumulative hazard function)ctype\(\rightarrow\) method used to estimate cumulative hazard function (1=Nelson Aalen, 2=Fleming-Harrington)conf.type\(\rightarrow\) available options include (“none”, “plain”, “log” (default), “log-log”, and “logit”)
Example
mp6 <- c(6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 9, 10, 10, 11, 13, 16, 17,
19, 20, 22, 23, 25, 32, 32, 34, 35)
plc <- c(1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 8, 8, 8, 8,
11, 11, 12, 12, 15, 17, 22, 23)
gehan65 <- tibble(
time = c(mp6, plc),
status = c(1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0,
0, 1, 1, rep(0, 5), rep(1, 21)),
drug = c(rep("6-MP", 21), rep("placebo", 21))
)
glimpse(gehan65)Rows: 42
Columns: 3
$ time <dbl> 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 9, 10, 10, 11, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 22, 23, 25, 3…
$ status <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, …
$ drug <chr> "6-MP", "6-MP", "6-MP", "6-MP", "6-MP", "6-MP", "6-MP", "6-MP",…gehan65 %>%
count(drug, status)# A tibble: 3 × 3
drug status n
<chr> <dbl> <int>
1 6-MP 0 12
2 6-MP 1 9
3 placebo 1 21- No censored time for Placebo group.
# keep only the Treatment Group
dat6MP <- gehan65 %>%
filter(drug == "6-MP")# Fitting model for the Treatment Group without any covariate
mod1 <- survfit(Surv(time = time, event = status) ~ 1,
conf.type = "plain",
data = dat6MP)- Default
conf.typeislog
# Produces summary of the KM fit
summary(mod1)Call: survfit(formula = Surv(time = time, event = status) ~ 1, data = dat6MP,
conf.type = "plain")
time n.risk n.event survival std.err lower 95% CI upper 95% CI
6 21 3 0.857 0.0764 0.707 1.000
7 17 1 0.807 0.0869 0.636 0.977
10 15 1 0.753 0.0963 0.564 0.942
13 12 1 0.690 0.1068 0.481 0.900
16 11 1 0.627 0.1141 0.404 0.851
22 7 1 0.538 0.1282 0.286 0.789
23 6 1 0.448 0.1346 0.184 0.712Kaplan-Meier plots
# This produces the KM plot; but it is not nice.
plot(mod1)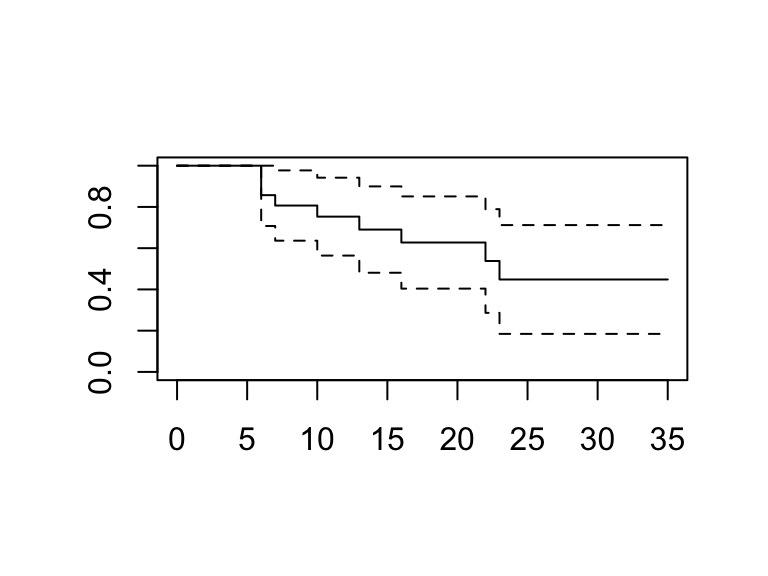
- We’ll use the
ggplot2package for nicer plots.
broom::tidy(mod1) # A tibble: 16 × 8
time n.risk n.event n.censor estimate std.error conf.high conf.low
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 6 21 3 1 0.857 0.0891 1 0.707
2 7 17 1 0 0.807 0.108 0.977 0.636
3 9 16 0 1 0.807 0.108 0.977 0.636
4 10 15 1 1 0.753 0.128 0.942 0.564
5 11 13 0 1 0.753 0.128 0.942 0.564
6 13 12 1 0 0.690 0.155 0.900 0.481
7 16 11 1 0 0.627 0.182 0.851 0.404
8 17 10 0 1 0.627 0.182 0.851 0.404
9 19 9 0 1 0.627 0.182 0.851 0.404
10 20 8 0 1 0.627 0.182 0.851 0.404
11 22 7 1 0 0.538 0.238 0.789 0.286
12 23 6 1 0 0.448 0.300 0.712 0.184
13 25 5 0 1 0.448 0.300 0.712 0.184
14 32 4 0 2 0.448 0.300 0.712 0.184
15 34 2 0 1 0.448 0.300 0.712 0.184
16 35 1 0 1 0.448 0.300 0.712 0.184broom::tidy(mod1) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_step(aes(time, estimate))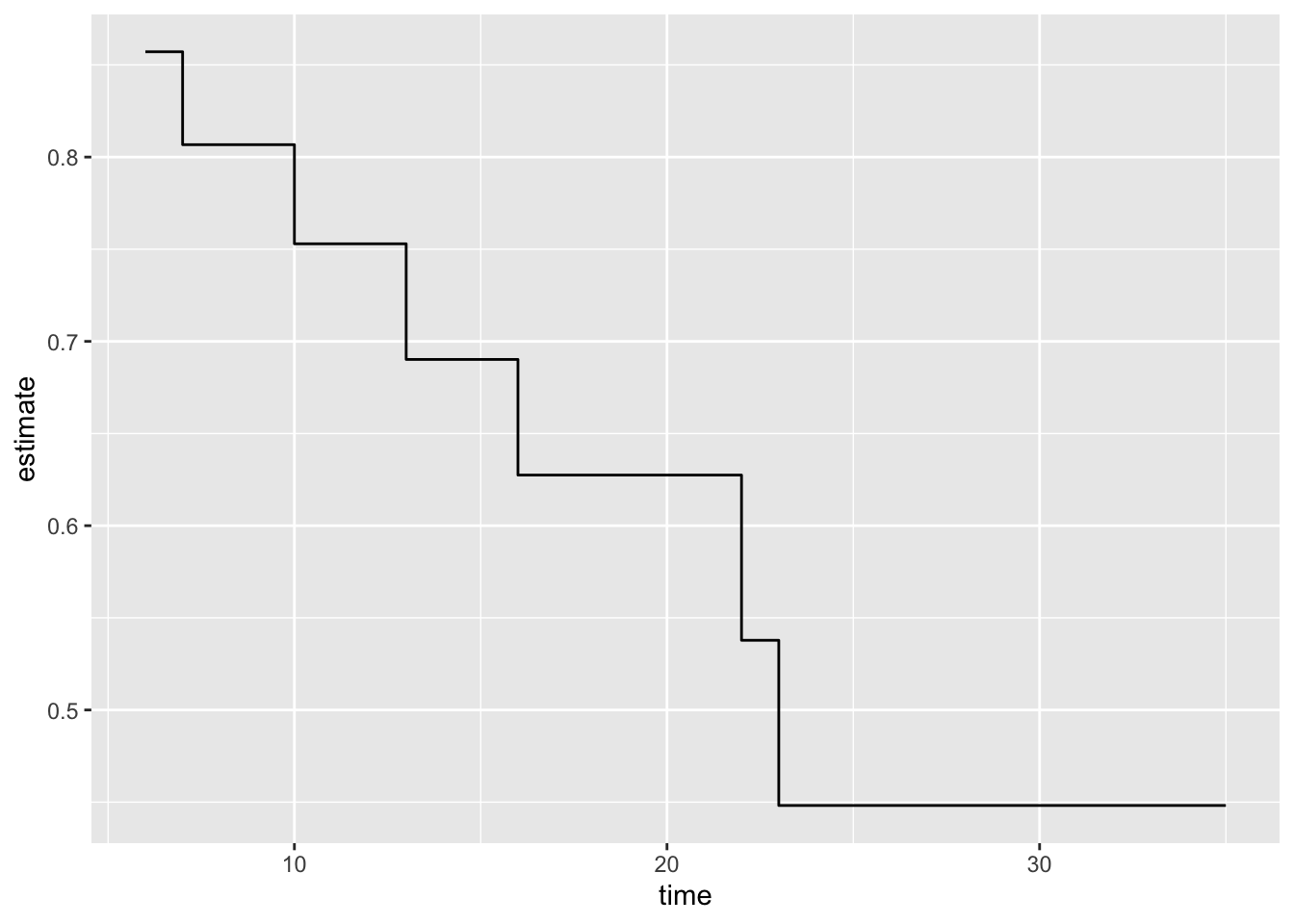
tidy(mod1) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_step(aes(time, estimate)) +
geom_step(aes(time, conf.high), linetype = "dotted", col = "red") +
geom_step(aes(time, conf.low), linetype = "dotted", col = "red")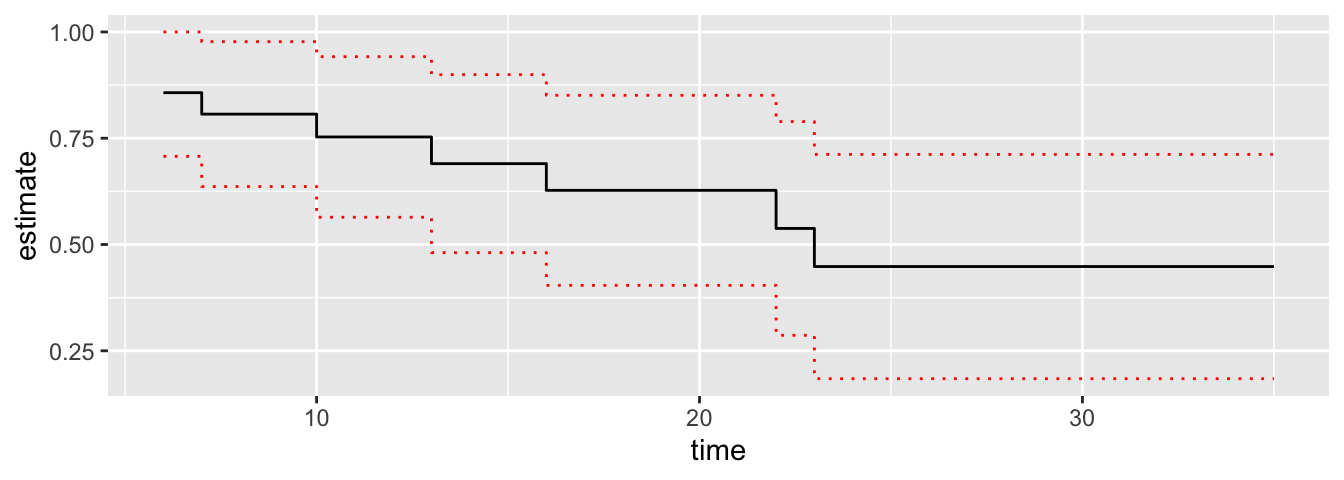
Estimating survival probability
- To estimate the probability of survival time, we use
summary()with thetimesargument.
summary(mod1, times = 10)Call: survfit(formula = Surv(time = time, event = status) ~ 1, data = dat6MP,
conf.type = "plain")
time n.risk n.event survival std.err lower 95% CI upper 95% CI
10 15 5 0.753 0.0963 0.564 0.942- So the probability of surviving to 10 years is 0.75.
- We can produce nice publication-ready tables of survival probability estimates using the
tbl_survfit()function from thegtsummarypackage
mod1 |>
gtsummary::tbl_survfit(
times = 10,
label_header = "**10-year survival (95% CI)**"
)| Characteristic | 10-year survival (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| Overall | 75% (56%, 94%) |
Estimating quantiles
$quantile
20 25 50 75 80
10 13 23 NA NA
$lower
20 25 50 75 80
6 6 13 23 23
$upper
20 25 50 75 80
22 23 NA NA NA - So, first quartile is 13. Median is 23.
- We can produce nice publication-ready tables of median survival time estimates using the
tbl_survfit()function from thegtsummarypackage
mod1 %>%
gtsummary::tbl_survfit(
probs = 0.5,
label_header = "**Median survival (95% CI)**"
)| Characteristic | Median survival (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| Overall | 23 (13, —) |
Fitting model with a covariate
mod2 <- survfit(
Surv(time = time, event = status) ~ drug,
data = gehan65,
conf.type = "plain"
)broom::tidy(mod2) # A tibble: 28 × 9
time n.risk n.event n.censor estimate std.error conf.high conf.low strata
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 6 21 3 1 0.857 0.0891 1 0.707 drug=6-MP
2 7 17 1 0 0.807 0.108 0.977 0.636 drug=6-MP
3 9 16 0 1 0.807 0.108 0.977 0.636 drug=6-MP
4 10 15 1 1 0.753 0.128 0.942 0.564 drug=6-MP
5 11 13 0 1 0.753 0.128 0.942 0.564 drug=6-MP
6 13 12 1 0 0.690 0.155 0.900 0.481 drug=6-MP
7 16 11 1 0 0.627 0.182 0.851 0.404 drug=6-MP
8 17 10 0 1 0.627 0.182 0.851 0.404 drug=6-MP
9 19 9 0 1 0.627 0.182 0.851 0.404 drug=6-MP
10 20 8 0 1 0.627 0.182 0.851 0.404 drug=6-MP
# ℹ 18 more rowsbroom::tidy(mod2) %>%
select(time, estimate, strata)# A tibble: 28 × 3
time estimate strata
<dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 6 0.857 drug=6-MP
2 7 0.807 drug=6-MP
3 9 0.807 drug=6-MP
4 10 0.753 drug=6-MP
5 11 0.753 drug=6-MP
6 13 0.690 drug=6-MP
7 16 0.627 drug=6-MP
8 17 0.627 drug=6-MP
9 19 0.627 drug=6-MP
10 20 0.627 drug=6-MP
# ℹ 18 more rowsbroom::tidy(mod2) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_step(aes(time, estimate, col = strata)) 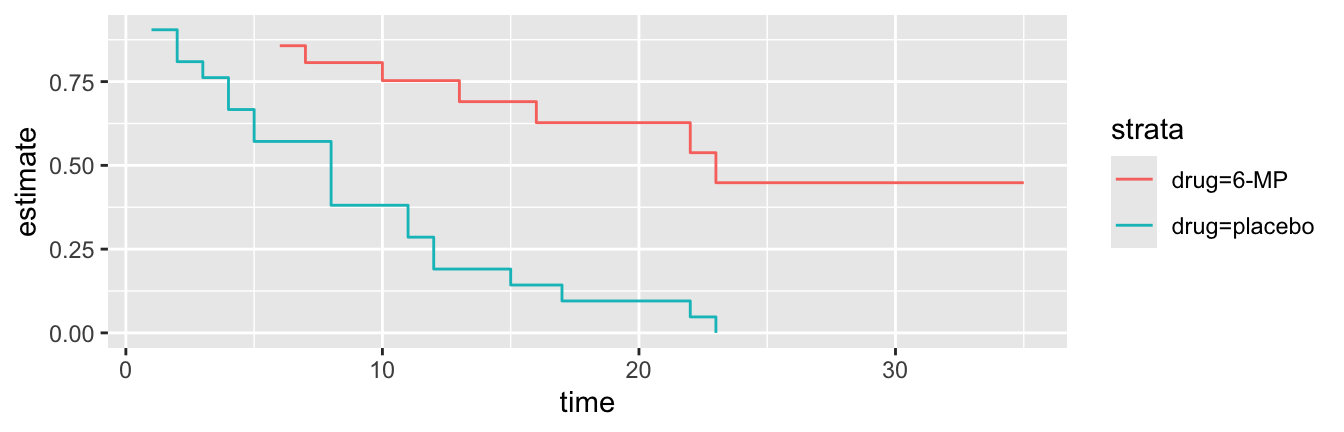
mod2 %>%
gtsummary::tbl_survfit(
times = 10,
label_header = "**10-year survival (95% CI)**"
)| Characteristic | 10-year survival (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| drug | |
| 6-MP | 75% (56%, 94%) |
| placebo | 38% (17%, 59%) |
mod2 %>%
gtsummary::tbl_survfit(
probs = 0.5,
label_header = "**Median survival (95% CI)**"
)| Characteristic | Median survival (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| drug | |
| 6-MP | 23 (13, —) |
| placebo | 8.0 (4.0, 11) |